Stable Rupiah, Steady Growth: Inside Bank Indonesia's Latest Rate Decision
Bank Indonesia held its key interest rate at 6.25% to stabilize the rupiah and attract FX inflows, while maintaining interventions in the FX and bond markets. Inflation remains within target, and GDP growth forecasts are steady. Future rate cuts depend on US Federal Reserve actions. A 25bps cut is expected in end-2024.
Figure 1: Indonesia Consumer Price Inflation and Policy Rate (%)
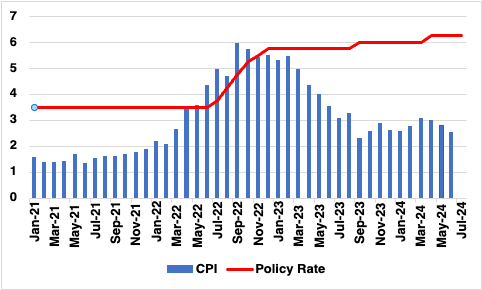
Source: Continuum Economics
In an anticipated move, Bank Indonesia (BI) decided to keep its key seven-day reverse repo rate unchanged at 6.25% during its monetary policy committee (MPC) meeting held on July 16-17. This decision, which aligns with our forecasts, underscores the central bank's commitment to stabilising the rupiah exchange rate and attracting foreign exchange (FX) inflows. In addition to maintaining the seven-day reverse repo rate, BI also kept the deposit facility rate at 5.50% and the lending facility rate at 7.00%. The central bank justified these decisions by emphasizing the need for stability in the foreign exchange market.
To support the rupiah, BI has reiterated its commitment to its triple intervention strategy. This includes interventions in the FX spot market, the Domestic Non-Deliverable Forwards (DNDF) market, and the secondary market for government bonds. Moreover, the central bank will continue issuing bonds such as SRBI, SVBI, and SUVBI securities to further support the exchange rate. The rupiah has appreciated by 1.21% since the end of June, though it has still depreciated by 4.84% year-to-date. BI highlighted that the rupiah has outperformed other regional currencies such as the Philippine peso, Thai baht, and South Korean won, which have experienced more significant depreciations.
On the inflation front, Indonesia’s Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation remains well within the central bank's target range of 2.5% ±1%, standing at 1.90% year-on-year as of June. Core inflation is even lower, suggesting that inflationary pressures are not currently a primary concern for monetary policy adjustments. Regarding economic growth, BI has maintained its GDP growth forecast at 4.7-5.5% for 2024. The central bank expects fiscal stimulus measures to bolster economic activity in the latter half of the year, complemented by a recovery in exports driven by increased demand from major trading partners. Although, with China's latest performance below expectation, the recovery maybe gradual.
Looking ahead, it appears likely that BI will maintain its current stance in the near term. The potential for rate cuts will depend on the monetary policy actions of the US Federal Reserve.