India CPI Preview: Food prices to weigh on headline CPI
Bottom line: India's inflation rate for October is projected to rise to 5.7% y/y due to base effects and domestic food prices. In the short term, global crude oil prices and domestic food price surge may pressure inflation further. The Reserve Bank of India is anticipated to maintain a neutral monetary stance, likely keeping the policy rate steady at 6.5% until December 2024.
Figure 1: India Consumer Price Inflation and Policy Rate (%)
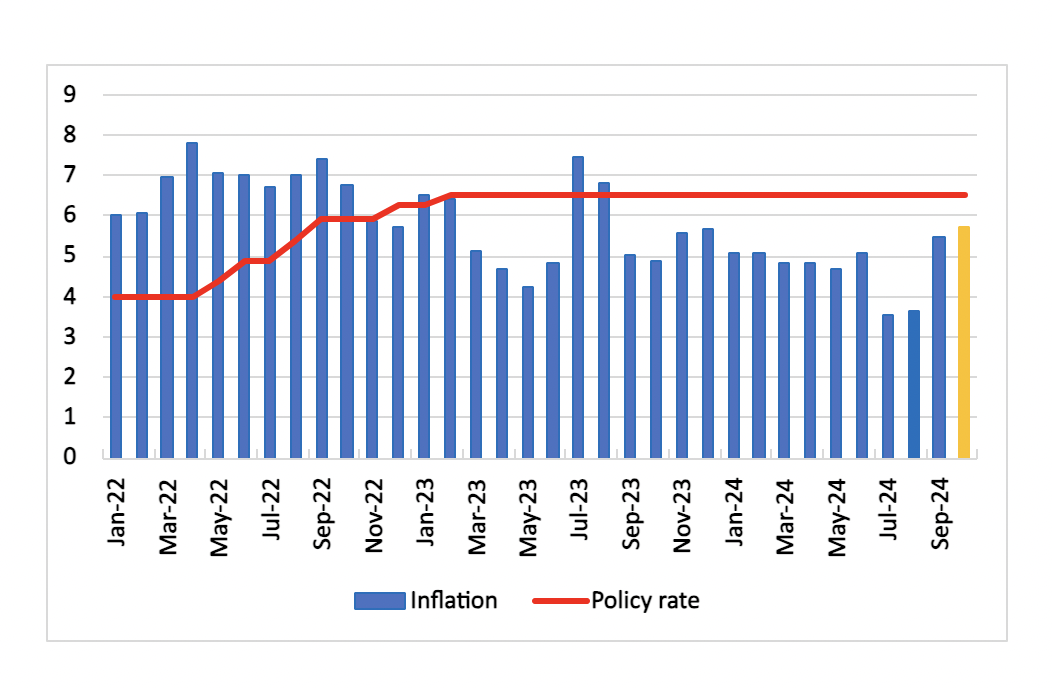
Source: MOSPI, Reserve Bank of India, Continuum Economics
Consumer price inflation (CPI) in India is expected to reach 5.7% y/y in in October 2024, driven predominantly by surging prices in food items, particularly vegetables and edible oils. This increase is slightly below the Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) upper tolerance threshold of 6%. This uptick will mark a second consecutive month of surge in price level.
Food prices constitute nearly half of the CPI basket, and their rapid increase has been a significant factor in the overall inflation rise. Notably, tomato and onion prices have reportedly surged by double digits due to unseasonal rains that disrupted production. Furthermore, the Indian government's decision to raise import taxes on edible oils by 20 percentage points in mid-September has exacerbated price increases, putting additional strain on household budgets.
Meanwhile, speaking at various events, RBI Governor Shaktikanta Das has acknowledged the upside risks to inflation, dampening expectations for an immediate rate cut. Given the latest inflation surge, it is likely that the RBI may further defer a rate cut to 2025. Substantial reductions in repo rate may be delayed until early next year due to persistent inflation levels not expected to return to the medium-term target of 4% until at least 2026. For now though, we still expect a 25bps cut in December.