Strong Military Spending and Investment Growth Help Russian Economy Expand by 3.4% YoY in July
Bottom Line: According to the preliminary figures announced by the Russian Ministry of Economic Development, Russia's GDP grew by 3.4% YoY in June after expanding by 3% YoY in June driven by military production and investments. We foresee Russian economy will expand by 2.5% in 2024 despite aggressive monetary policy, sanctions, tight labor market conditions and higher price pressures remain restrictive. The recent cross-border offensive by Ukraine inside Russia's western Kursk region could further pump up Russian military expenses in Q3 and Q4 contributing to GDP growth in H2.
Figure 1: GDP Growth (%, Annual), January 2023 – July 2024
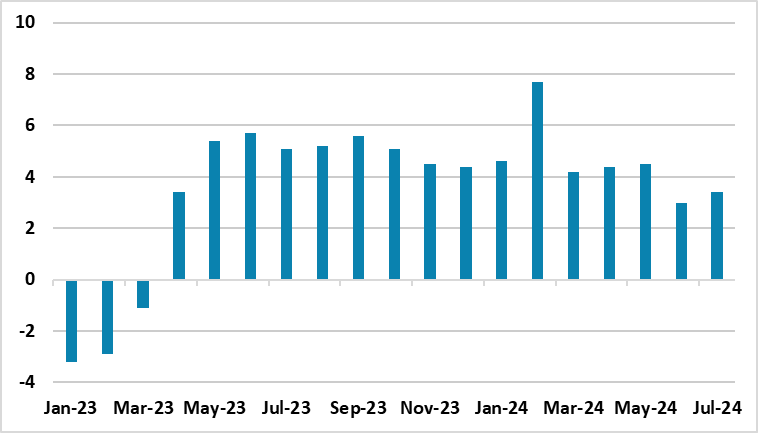
Source: Ministry of Economic Development
Russian economy continued its strong growth pattern in July, and grew by 3.4% YoY backed up by fiscal stimulus, strong military spending and investments despite the fact that economy is still strained by sanctions, export controls, high inflation, and tight labor market conditions. Driven by military production, industrial output rose by 3.3% YoY in July compared with a 2.7% increase the previous month, and by 3.1% when compared with the same period last year.
It appears the consumer activity remains high, shortage of labor resources persists and investments stay strong supported by both government incentives and high company profits. Unemployment remained at a historically low level of 2.4% in July. (Note: Statistics show that real wages rose 6.2% YoY in June, following an 8.8% increase in the previous month, while average nominal wages rose 15.3% YoY).
Speaking about the investments, deputy prime minister Novak said on August 28 that the growth of investments in H1 2024 demonstrated resilience of the Russian economy, and emphasized that “(…) growth of investments are stimulated by the business support from the government, as the institutional environment in the country improved significantly and incentives for investments accordingly moved up." Additionally, the Ministry of Economic Development also expects that investments will grow as of the end of 2024 above the current forecast figures thanks to improved support mechanisms, deputy minister Kryuchkova said recently.
When military spending, strong investments and fiscal stimulus are considered, it is worth noting that expenses continue to be met by growing budget revenues despite Western economic sanctions and problems with international payments. President Putin said on August 26 that Russia's budget revenues grew by 36% in the first 7 months of this year compared to the same period last year and reached around 20 trillion rubles ($218.78 billion). Putin also added that the Russian economy continues to grow at a high rate this year, with GDP growing by 4.6% in H1 as industrial production grew by 4.4% and the manufacturing industries expanded by 8% in H1.
Central Bank of Russia (CBR) announced on August 29 that economic overheating will start declining in H2 2024 facilitated by the tightened monetary policy, and projected that the economy will grow by 3.5-4% in 2024. CBR expects the economy will return to the trajectory of balanced growth of 1.5-2.5% in 2027 as the growth rates of consumer and investment demand will become more moderate in coming years.
Considering that economic growth is primarily driven by war-time activities and related subsidies, we think the recent cross-border offensive by Ukraine inside Russia's western Kursk region could further pump up Russian military expenses in Q3 and Q4, igniting higher a growth figure in 2024. We expect economic overheating to start contracting gradually in Q4 due to ongoing aggressive monetary tightening as high inflation rate, sanctions and military focus pose risks to Russia's economic stability.