U.S./China Trade Truce Reduce Downside and Extra Stimulus Prospects
The alternative hard landing scenario in China has been reduced significantly with the trade truce with the U.S. However, China will still have to cope with a minimum 30% overall tariff, with only around a 10% reduction in the fentanyl tariff likely to be agreed in the coming months. Our baseline for an overall trade agreement is Q4 2025 for Q1 2026 implementation and this prolongs the impact of moderately high tariff rates in 2025. Extra fiscal policy expansion will also be less and we stick with a 4.2% 2025 GDP growth forecast.
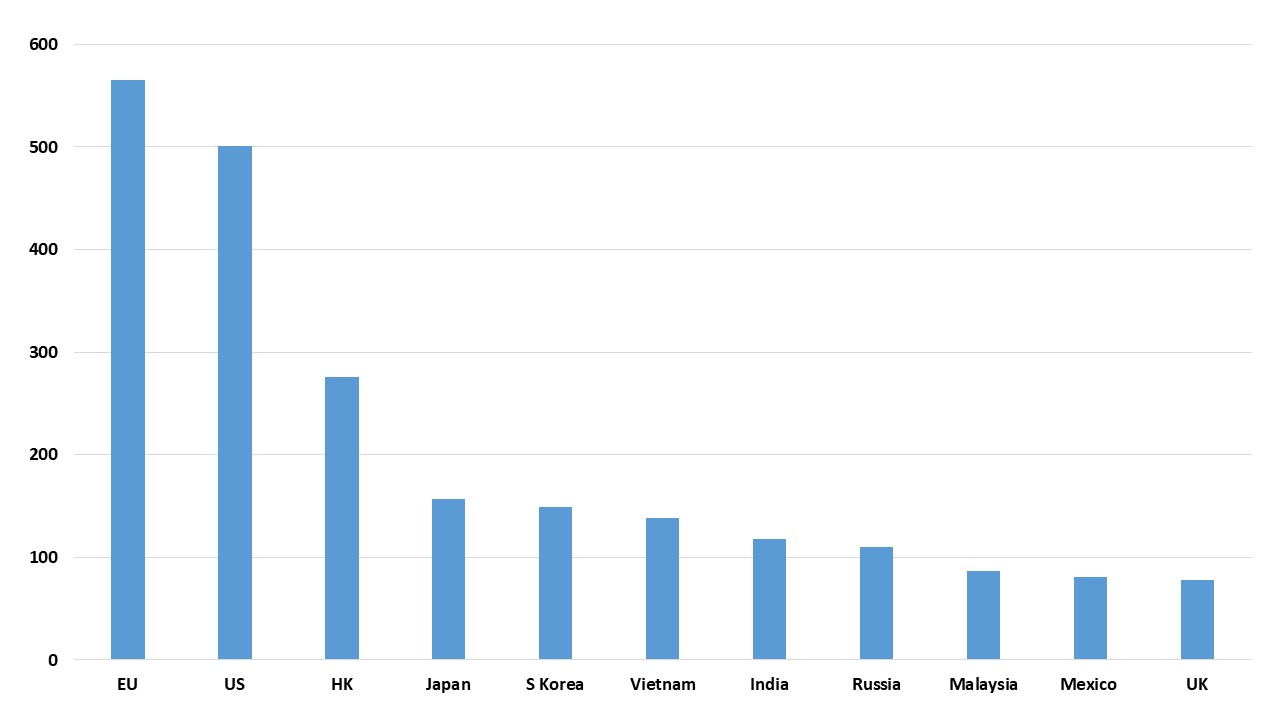
Figure 1: China Exports by Country 2023 (USD Blns)
Source: Comtrade
The agreement with the U.S. to put reciprocal tariffs at 10% for 90 days is lower than expected (here) and can be enough to restart frozen trade between China and the U.S. Though China effective rate is higher with the additional 20% for fentanyl, the U.S. hints in Geneva were that China will now likely take action and this could lead to a reduction in this tariff. We would see scope for the fentanyl tariff to be reduced to 10% within the next 90 days and then zero when a wider U.S./China trade deal is done. This all reduces the risk of a harder landing to 3.0-3.5% for China economy. However, it also reduces the urgency for China’s authorities to announce additional monetary and fiscal stimulus.
For now we keep the 4.2% GDP forecast for 2025 for a number of reasons.
• April trade freeze and ongoing tariff effects. The April surge in reciprocal tariffs by the U.S. will likely hurt Q2 GDP numbers, with anecdotal evidence suggesting almost a freeze is some U.S. exports. While some export diversions could have occurred to other main trading partners (Figure 1), this is likely to have been modest. The May 12 relief will help exports to the U.S. recover, but at a minimum 30% tariff for most goods. This remaining tariff will slow export growth to the U.S.
• Prolonged trade negotiations before deal. While we do see scope for a 10% reduction in the fentanyl rate, the Trump administration is very keen for political and strategic reasons to impose 25% on pharmaceuticals on all countries and this should be seen in the coming weeks. A trade deal could reduce the reciprocal/fentanyl tariff to 15-20%, but would require concessions from China that will likely take 3-9 months to agree. The 90 day deadline will likely be delayed by a further 90 days in August. China could easily buy more oil/LNG/chemicals and soybeans from the U.S. provided they do not become too dependent on the U.S. However, the U.S. earlier this year wanted a phase 2 trade deal with penalties if import or trade deficit reduction targets were not meet. This could lead to disputes in the coming months and prolonged negotiations. Our baseline is agreement Q4 2025 for Q1 2026 implementation and this prolongs the impact of moderately high tariff rates in 2025. Trade policy uncertainty will also impact China business investment as well.
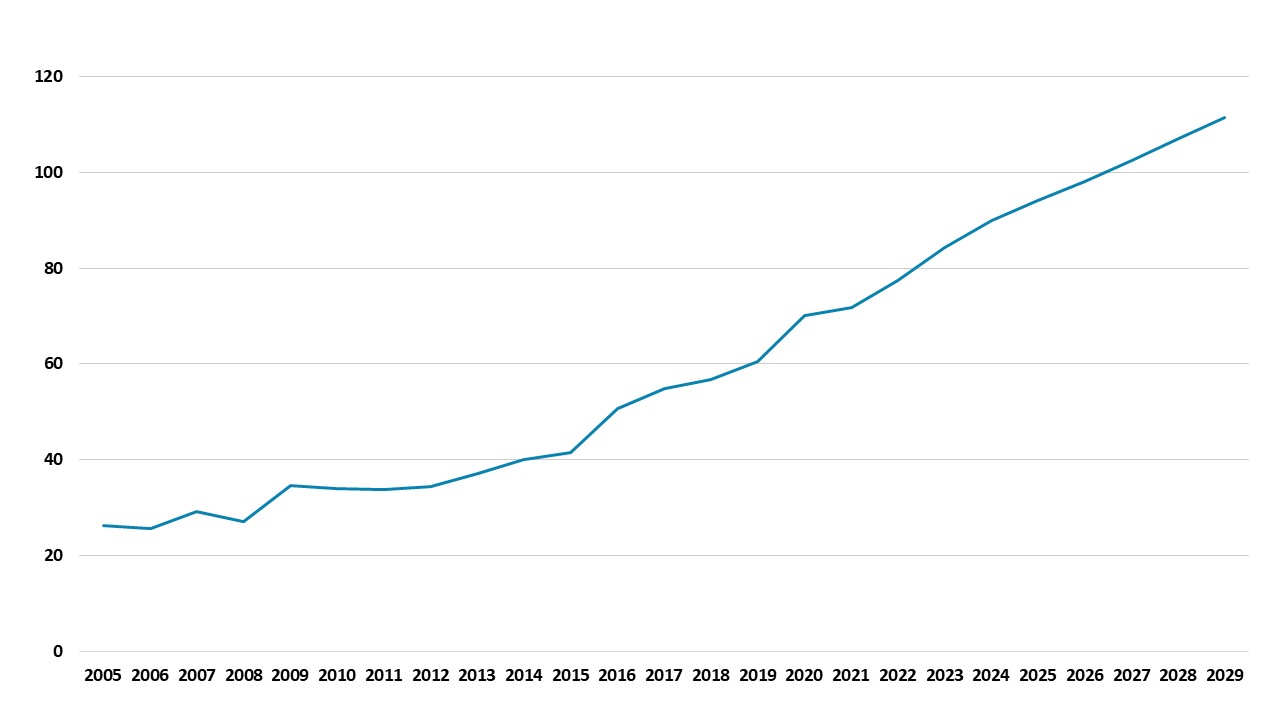
• Fiscal easing in 2025 has been below expectations at around Yuan2.5trn. Part of the reason is that the authorities feel constrained by the wider surge in government debt (Figure 2) than the official figures show. China authorities also constantly worry about the total government/corporate and household/GDP that has surged since 2007 to over 300% and above the U.S. and EZ. With the hard landing scenario reduced, this likely now means only an additional Yuan1trn extra fiscal expansion later this year rather than Yuan2trn. Official rates and RRR could also be cut more slower in H2 2025.
Figure 2: China Government Debt/GDP (%)
Source: IMF/Continuum Economics (IMF central measure article IV Aug 2024)