India CPI Preview: Inflation to Surge as Base Effects Fade
Bottom line:India’s September inflation level is expected to trend up to 4.1% y/y, given base effects. Global crude oil prices and heightened geopolitical tensions pose risks to inflation in the near term. Meanwhile, monetary policy is expected to remain tight and policy rate to be retained at 6.5% in the upcoming October decision.
Figure 1: India Consumer Price Inflation and Policy Rate (%)
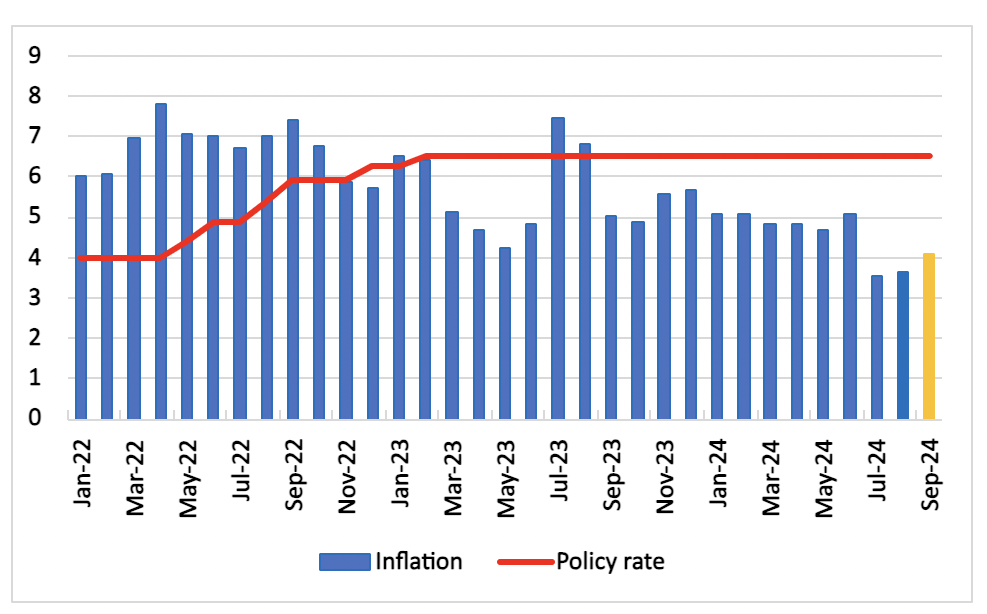
Source: MOSPI, Reserve Bank of India, Continuum Economics
India's retail inflation is expected to rise to 4.3% y/y in September 2024, up from 3.65% in August. This increase is largely due to the reversal of base effects, which had kept inflation below 4% during July and August. While food inflation, particularly driven by a seasonal surge in vegetable prices, had spiked in recent months, we anticipate food pressures to have eased slightly in September. However, food inflation is still projected to remain high given expected increased in specific food items (cereals, pulses).
It is worth noting that September is a lean season in India given lower discretionary spending during a 16-day period. As a consequence, demand is expected to have remained subdued during the month. Despite lower demand, inflation is expected to have trended upward, as the base effect drops out of th equation. Meanwhile, the October Monetary Policy Committee meeting is underway. In our view, the MPC will closely monitor the kharif harvest and food inflation trajectory in the coming months. While inflationary pressures persist, we maintain our forecast that the RBI could consider a rate cut by December if inflation stabilises. However, geopolitical tensions in West Asia and rising crude oil prices will stoke inflation in the coming weeks.