Argentina: Milei’s Plan Going Smoothly
Since taking office, Milei's administration has focused on tackling Argentina's fiscal and monetary imbalances, implementing a shock fiscal plan to reduce expenditures by 4% in 2024. Fiscal surpluses have been recorded monthly, but the adjustment has caused three consecutive quarters of economic contraction. The central bank has adopted a crawling-peg for the ARS, stabilizing the exchange rate, though capital controls remain. Despite economic challenges, Milei’s approval remains stable, and his political party is gaining strength ahead of 2025 midterm elections.
Figure 1: Argentina Economic Activity Index (Seasonally Adjusted)
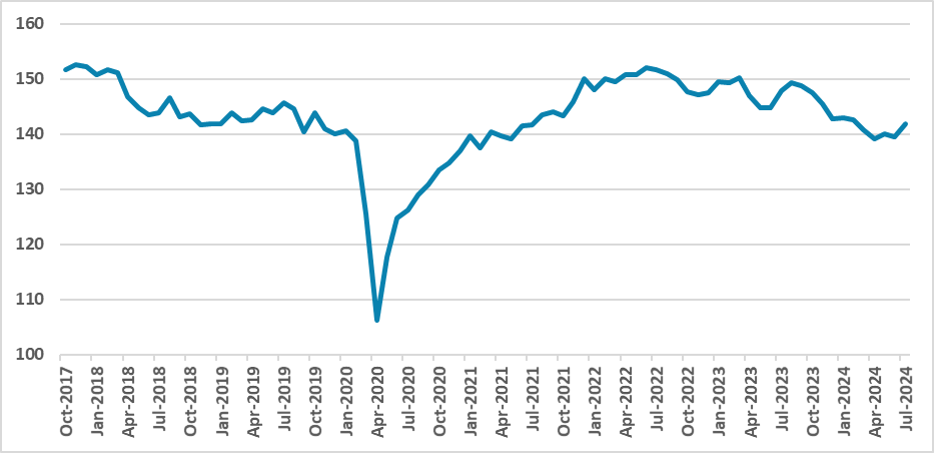
Source: INDEC
Since taking office, Milei’s administration has focused on addressing Argentina’s macroeconomic imbalances. The diagnosis centered on large fiscal deficits, which have consistently been financed by printing new Pesos to cover the shortfall. Additionally, the imbalance between exports and imports has typically led to a USD deficit, depleting financial reserves.
Figure 2: Argentina CPI (m/m, %)
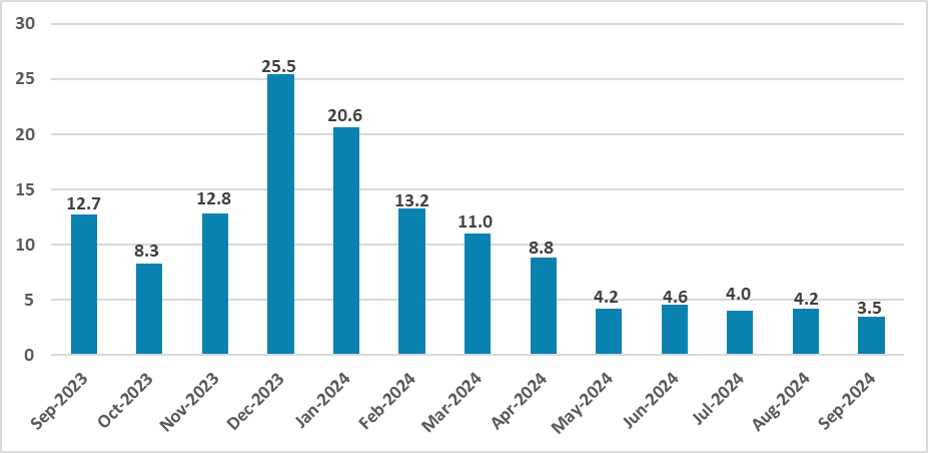
Source: INDEC
Milei’s plan involved implementing a shock fiscal strategy, reducing expenditures by around 4% in 2024. The resulting fiscal surplus would enable the shutdown of the central bank’s “printing machine.” So far, results show that the government has been able to register fiscal surpluses in every month of the year. However, this fiscal consolidation has come at a cost. The substantial fiscal adjustment has severely impacted economic activity, resulting in three consecutive quarters of contraction. This has squeezed domestic demand, and, coupled with a recovery in agricultural exports, has allowed the government to marginally increase its reserves.
Figure 3: Argentina Fiscal Surplus (ARS Millions)
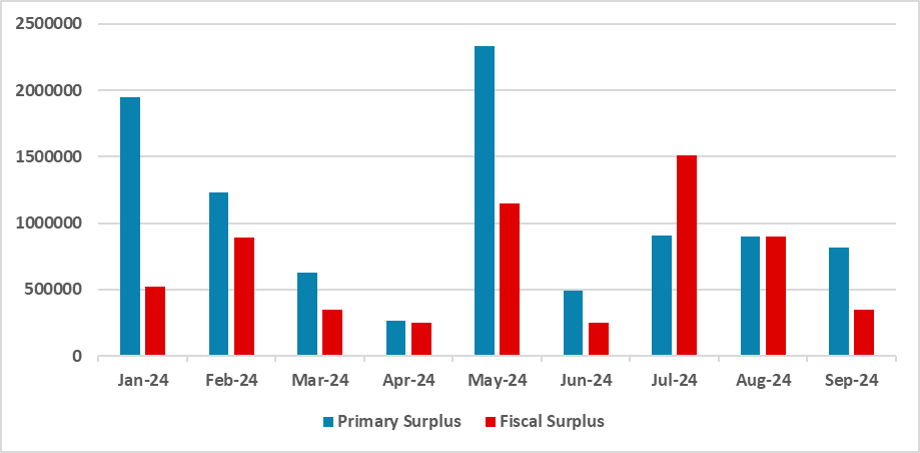
Source: Finance Ministry
In monetary terms, the central bank is now focused on cleaning up its balance sheet, relying on the fiscal anchor to control inflation. After devaluing the ARS in December, the government adopted a 2% per month crawling-peg for the exchange rate. While capital controls remain in place, some interventions have been made to reduce the gap between the multiple exchange rates. So far, the BLUE (parallel) rate has stabilized around 1200 ARS/USD, with the gap between the official and BLUE rates narrowing to approximately 17%. The government aims to lift capital controls, although no specific date has been set. We believe the conditions will emerge in the second half of 2024 when central bank foreign reserves are expected to be higher.
Figure 4: Argentina Exchange Rate
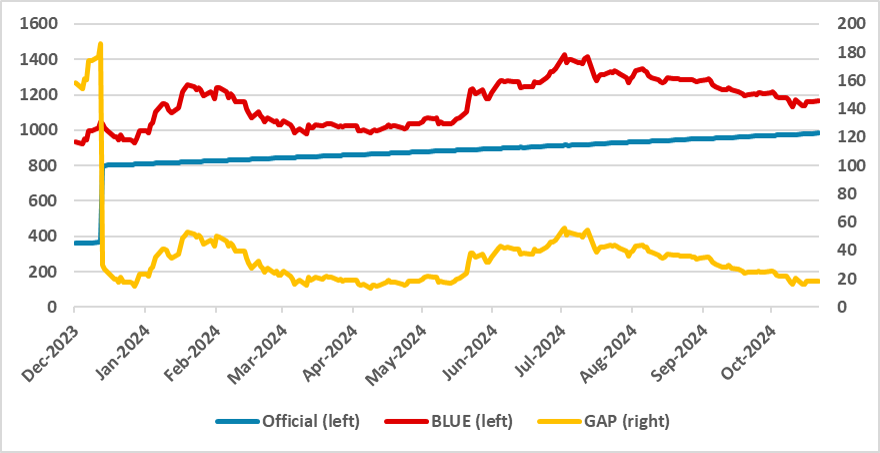
Source: Refinitiv and Continuum Economics
Despite the poor economic performance in 2024, it appears that the population views this as a necessary step toward stabilization. Javier Milei’s approval ratings have not dropped significantly, and his political force has achieved some notable victories in Congress, maintaining vetoes on proposals that would increase government spending. It remains to be seen whether there will be a recovery in 2025, but early polls indicate that Milei’s political party, "La Libertad Avanza," may increase its representation in Congress in the midterm elections.
Figure 5: Central Bank International Reserves (USD Millions)
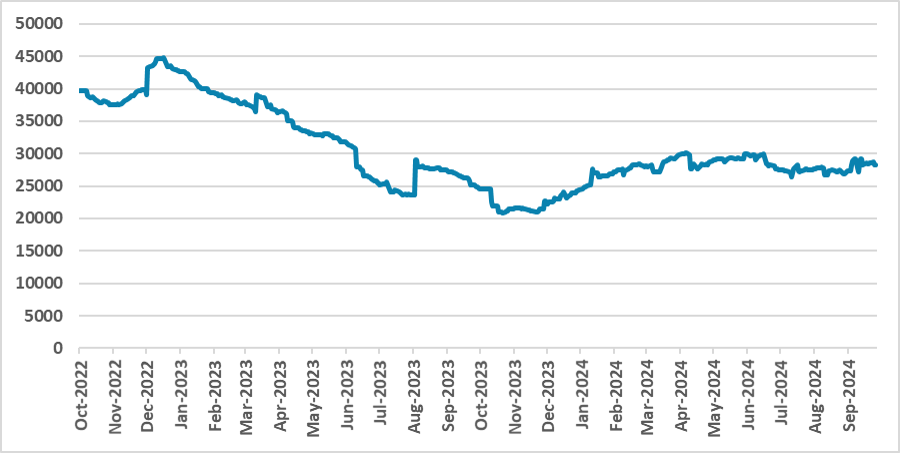
Source: BCAR