Indonesia CPI Preview: Food Prices to Push Up CPI in April
Indonesia’s consumer price inflation in expected to continue to trend upward in April. Food prices, alongside higher transportation price growth will drive up inflation. Furthermore, increased demand during Ramadan will also weigh on headline inflation.
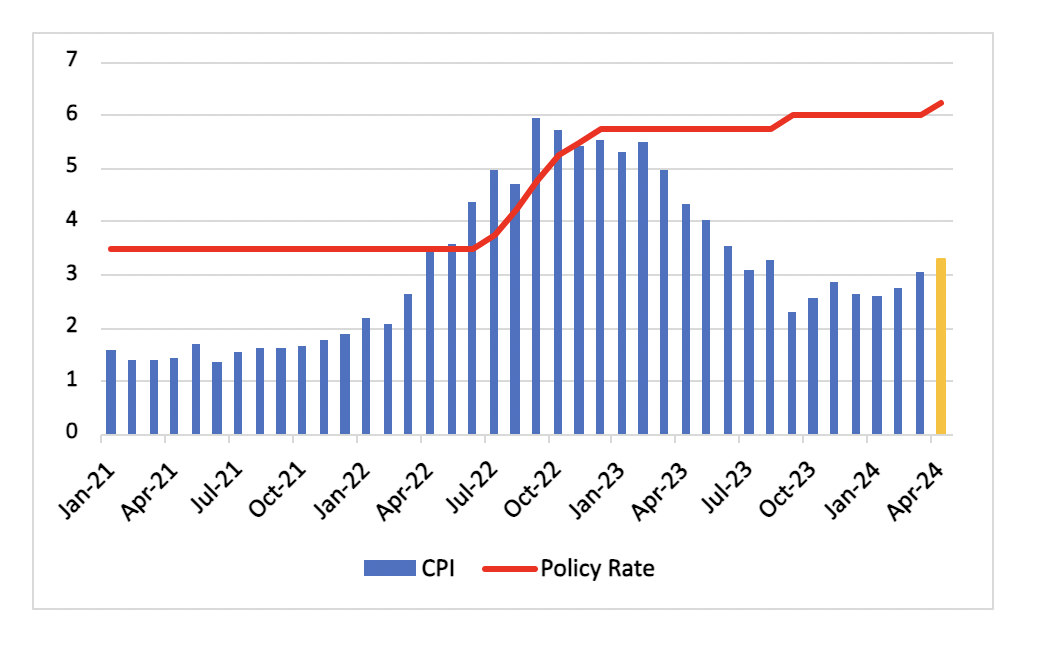
Figure 1: Indonesia Consumer Price Inflation and Main Policy Rate (%)
Source: Continuum Economics
Indonesia experienced a bump in consumer price inflation, with a rise to 3.1% yr/yr in March, up from 2.8% in the preceding month. Meanwhile, core inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, saw a slight uptick from 1.7% to 1.8%. We anticipate further inflationary momentum in April, followed by a slowdown starting in the third quarter of the year. As seen in in March, food prices will remain the main driving factor of rising inflation. Food inflation rose 7.4% yr/yr in March. The inflationary risks remain elevated until mid-2024, propelled by a significant increase in rice prices, which soared by 20% yr/yr in March. Additionally, delayed harvests due to the lingering effects of last year's El Niño and subsequent floods in Java and Sumatra are exacerbating the domestic rice supply shortage.
To counterbalance this, the government plans to increase rice imports to 3.6 million tonnes in 2024, up from 3.1 million tonnes in 2023. However, global rice prices remain elevated, especially as India's ban on rice exports sustains. Moreover, the Ramadan period in March and April, coupled with the anticipated large-scale "mudik / balik" migration, is expected to further strain inflation, particularly in transportation and food sectors. Looking ahead, the recent depreciation of the rupiah against the US dollar, amid US dollar strength, elevated geopolitical tensions and speculation about potential changes in key government positions, adds another layer of uncertainty. It is anticipated that inflation will remain above 3% yr/yr in April, coming in at 3.3% yr/yr during the month. Headline inflation is expected to ease from May, as the effects of the recent rate hike kicks in.