Russian Economy Expands by 4.2% YoY in March, and 5.4% in Q1
Bottom Line: According to the figures announced by the Russian Ministry of Economic Development, Russia's GDP grew by 4.2% YoY in March owing to strong fiscal stimulus, high military spending, invigorating consumer demand and investments. We now foresee Russian economy will expand by 2.6% in 2024 driven in part by a significant increase in military spending due to likely intensified Russian offensive operations in Ukraine this summer, oil export volumes holding steady and surges in corporate investment and private consumption, despite tight monetary policy, higher price pressures, and tight labor market remain restrictions.
Figure 1: GDP Growth (%, Annual), 2014 - 2023
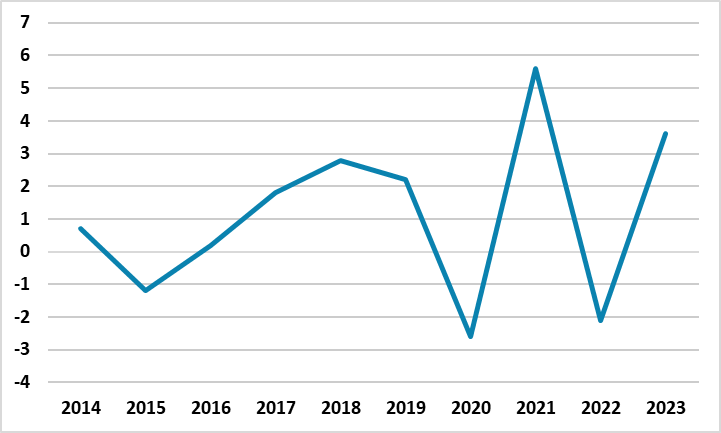
Source: Continuum Economics
After expanding by 3.6% YoY in 2023, Russian economy continued its strong growth trend in March and grew by 4.2% YoY particularly due to fiscal stimulus, increased military spending and investment (gross fixed capital formation) coupled with strong household consumption, despite the economy remains strained by economic sanctions, export controls, high inflation, tight labor market conditions, and a volatile Ruble (RUB). (Note: The weakening of RUB accelerated particularly after March 11 as the currency lost 2.4% of its value against the USD between March 11 and April 10).
Ministry of Economic Development also announced that the Russian GDP surged by 5.4% in Q1 2024. A department director at the Ministry of Economic Development, Denisov said that "Q1 growth has been stimulated by the rise in salaries taking into account low unemployment. Information and communications, construction and processing facilities are among industries with the highest rate of growth in salaries, which are concurrently drivers of economic development."
As Russia continues to grow beyond expectations, we saw international and domestic institutions revised Russia growth predictions particularly in April. IMF’s WEO, which was published in April, demonstrated that the IMF lifted the forecast for Russia's economic growth to 3.2% in 2024 from 1.1% backed up strong military spending and consumption. IMF also specified that Russia's GDP growth is expected to dip to 1.8% in 2025 partly due to labor shortage exacerbated by the mobilization of hundreds of thousands of soldiers.
In addition to IMF, the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) upgraded Russia's GDP forecast to 2.6% from 1.8% for 2024. OECD believes that the economy will grow by 1% in 2025.
Additionally, Central Bank of Russia (CBR) Governor Nabiullina said told at a press conference late April that the tight monetary policy pursued by the CBR does not impede the development of the national economy or stifle it. If the level of the key rate is commensurate with other circumstances in the economy, then tight monetary policy has a much stronger effect on slowing inflation than on GDP dynamics, Nabiullina noted.
CBR upgraded its outlook on GDP growth for 2024 to 2.5-3.5% late April, when compared to previous predictions of 1-2%. The CBR emphasized that "High-frequency indicators show that, in Q1, the Russian economy continued to grow notably faster than forecast. Consumer activity remained high amid a significant increase in households’ incomes and positive consumer sentiment. According to companies’ surveys, investment demand remained high."
The Ministry of Economic Development improved the forecast for GDP growth in 2024 to 2.8% from the previously expected 2.3%. President Putin also highlighted at a meeting on economic issues on April 27 that the surge in growth and emphasized that Russian GDP may expand more than 3% by the end of 2024.
Financial Times also reported May 2 that Russian industrial output is on the rise, propelled by sectors such as metal products, machine building and chemical production which are partially attributed to the military-industrial complex. According to Financial Times, employment, income and tax collection are also all reaping the benefits of the war boom as Russia now boasts 6,000 military-industrial enterprises, when compared to less than 2,000 before the war while workforce in this sector has expanded significantly.
In line with abovementioned predictions, we now foresee Russian economy to expand by a moderate 2.6% in 2024, higher than our previous prediction of 1.9% driven in part by a significant increase in military spending due to likely intensified Russian offensive operations in Ukraine, oil export volumes holding steady and surges in corporate investment and private consumption. (Note: Our estimate stays at 1.1% for 2025).
Despite risks to the growth trajectory such as staff shortages, falling trend in the utilization rates, and higher price pressures likely muting private spending growth, and sanctions; we think the growth in H2 of 2024 will be mostly stimulated by likely higher military spending taking into account that the military analysts foresee Russian offensive operations in Ukraine will likely intensify in the upcoming months, probably after late May or June.