Strong Growth Trend Continues in Russia
Bottom Line: The Russian economy continued its strong growth trend, and expanded by 4.6% YoY in January 2024, thanks to high defense spending, continued consumer demand and lending, and growing wages, which also ignite increased demand and prices for products and services.
Figure 1: GDP Growth (%, Annual), 2014-2023
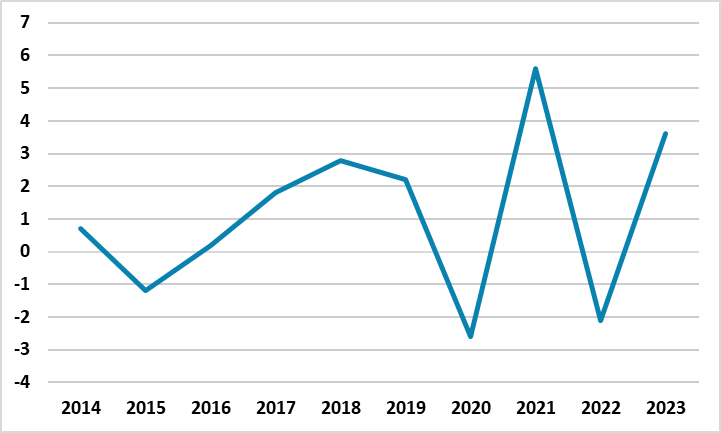
Source: Continuum Economics
After growing by 3.6% in 2023, the Russian economy expanded by a strong 4.6% YoY in January 2024. The main driver for the GDP growth remained the surge in the military spending, supported by the invigorating consumer demand amid greater outlays on social support, higher wages and strong consumer and corporate lending. Retail sales, which is a key indicator for consumer demand, surged by 9.1% YoY in January.
Russian labor market continues to remain very tight. Russian statistics service (Rosstat) recently announced that unemployment decreased to a record low 2.9% in January, a clear evidence of the labor shortage that is hampering the productivity. (Note: The real wages grew by 7.8% in 2023).
Speaking about the growth figures, first Deputy Prime Minister Andrey Belousov said on February 27 that the Economic Development Ministry’s outlook on Russia’s GDP growth rates for coming years is adequate, and indicated that "If we take the Economic Development Ministry’s forecast for the next six years, we can see that six years are divided into two stages. The first stage consisting of three years is the stage of structural transformation with growth rates of around 2% per year or slightly higher. Further on we get to a growing trajectory reaching around 3%, outpacing global economic growth rates though if it stands at 2.5%." First Deputy Prime Minister added that non-resource and non-energy exports should become one of the drivers of Russia’s economic growth in the future, demonstrating Russia’s intention to reorient its economy out of energy sector’s dominance.
In a similar vein, Economic Development Minister Maxim Reshetnikov also stated that Russia’s economy has recovered quicker than projected, with the current growth rates exceeding the worldwide average. Speaking about strong growth in 2023, Russian President Putin said the country's economy is successfully transitioning away from Western markets and expanding self-sufficiency while simultaneously cultivating new trading relationships.
According to the Economic Development Ministry’s forecast, Russia’s GDP will grow by 2.3% in 2024. Central Bank of Russia (CBR) projects GDP growth at 1-2%. Despite high expectations by the Russian authorities, we foresee Russian GDP to grow by 1.3% and 1.1% in 2024 and 2025, respectively, partly backed up by high military spending, and strong consumer and corporate lending.
We think the growth will be clipped due to strong monetary tightening by the CBR in 2023, which is still feeding through with lagged impacts. In line with our projections, CBR announced on February 27 that consumer demand continues to remain higher than expected, while it has recently started reacting to tight monetary policy. The Central Bank also pronounced on February 22 that the growth of the corporate loan portfolio paused in January, after its quick expansion by 1.8% in December 2023. As to mortgage lending, this segment recorded a notable decline whose growth rate dropped from 2.9% in December 2023 to 0.6% in January 2024.
We foresee other factors threatening growth trajectory in 2024 are severe staff shortages, falling trend in the utilization rates, and sanctions on Russia’s energy sales leading to a plummet in export revenues, coupled with growing imports. It is worth to mention that the country continues to be squeezed by high inflation and weakening RUB, which lost around 30% of its value against the dollar in 2023.
We continue to think the amount of the war spending would be the key determinant for the growth projections as military analysts believe Russian expenditure on defense will rise to around 6% of GDP in 2024 while it was 3.9% of GDP in 2023, and we envisage this can change the growth scene.