Russian Economy Expanded by a Fast 3.6% in 2023, Rosstat Reports
Bottom Line: According to Russian Statistics Service’s (Rosstat) announcement, the Russian economy grew by a strong 3.6% in 2023 from a revised 1.2% drop in 2022, thanks to fiscal stimulus, increased defense spending to boost industrial production, continued consumer demand and lending coupled with higher salaries despite the economy is strained by economic sanctions, high inflation, tight labor market conditions, weakening trade income, and volatile Ruble (RUB).
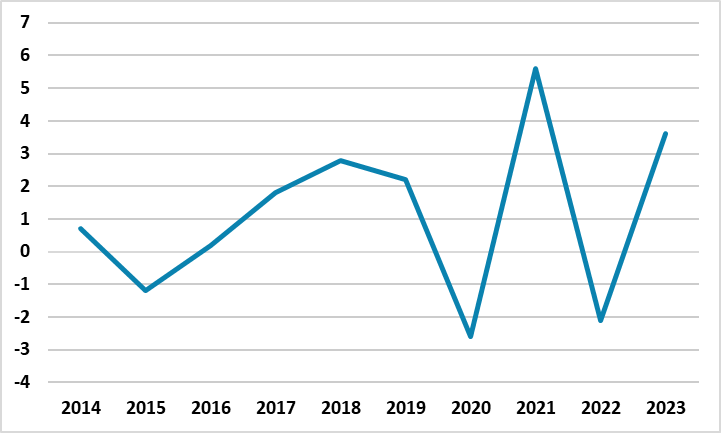
Figure 1: GDP Growth (%, Annual), 2014-2023
Source: World Bank, Continuum Economics
The Russian economy rebounded sharply from a slump in 2022, and expanded by a strong 3.6% in 2023, according to a recent announcement by Rosstat. The main driver for GDP growth remained the surge in the military spending and strong manufacturing activities, supported by the invigorating consumer demand amid greater outlays on social support, and higher wages. The social aids, benefits and bonuses by the government to the people who join the armed forces during the Ukraine war remained a prominent factor as the government continued to make social payments to the families for service persons who are killed or wounded.
Despite Central Bank of Russia’s (CBR) base-case scenario which forecasted GDP growth rates would reach 2.2-2.7% in 2023, the figures were stronger than expected almost one month before the presidential elections which will be held on March 17. Speaking about the growth, Russian President Putin has recently said the country's economy is successfully transitioning away from Western markets and expanding self-sufficiency while simultaneously cultivating new trading relationships.
In a similar vein, Russia’s prime minister Mikhail Mishustin said on January 30 that 2023 GDP growth may total up to 4% after revisions, driven by an increase in domestic consumer and investment demand, particularly thanks to implementation of national projects. Minister of Economic Development Maxim Reshetnikov also specified that "To support demand, we actively implemented import substitution programs. As a result, the manufacturing sectors focused on domestic demand made a significant contribution to the economy's growth in 2023."
After vigorous growth figures backed by military investments and spending in 2023, we foresee Russian GDP to grow by a moderate 1.3% and 1.1% in 2024 and 2025, respectively, taking into account strong monetary tightening by the CBR is still feeding through with lagged impacts. Other factors threatening growth and likely lead to a partial slowdown in 2024 are severe staff shortages, falling trend in the utilization rates, and sanctions on Russia’s energy sales leading to a plummet in export revenues, coupled with growing imports. It is worth to mention that the country continues to be squeezed by high inflation and weakening RUB, which lost around 30% of its value against the dollar in 2023.
It appears the amount of the war spending would be a significant determinant for the growth projections as military analysts believe Russian expenditure on defense will rise to around 6% of GDP in 2024 while it was 3.9% of GDP in 2023, and we think this can change the growth scene. (Note: According to official information, Russia spends 29% of all public expenditures on defense while the NATO average is only 4.3%, and we think this figure is probably larger when considering the reconstruction expenditures in occupied parts of Ukraine). On the sanctions front, the steep increase in military expenses raises questions concerning how effective the Western sanctions have been to depress Russian financial revenues.